
What is a tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction is a procedure that removes a diseased tooth that cannot be cured with other conservative methods, thus avoiding possible serious infections.
Tooth extraction can be simple or surgical. In most cases, when the teeth are easily accessible, this type of surgery is simple. Sometimes, however, it can become surgical if a certain amount of pressure must be applied to be able to remove the tooth or if a substantial part of the tooth crown is missing.
Why are teeth removed?
dental extraction is indicated in some specific cases of which:
- broken, fractured, cracked, deeply decayed teeth that cannot be rebuilt;
- periodontal teeth with an advanced degree of mobility;
- teeth with cysts and large granulomas that did not have a positive effect on treatment;
- teeth positioned incorrectly or misaligned from their correct position in the dental arch that cannot be straightened using orthodontic methods;
- included teeth;
- orthodontic purpose for a harmonious smile.
When the tooth becomes ill due to deep caries or when it is irreversibly damaged and no treatment can save it, dental extraction is resorted to.
Extraction of the diseased tooth prevent the spread of its infection to nearby teeth or even to the whole organism. Following extraction, bone loss, development and worsening of periodontal disease are also avoided.
Impacted teeth can often create a number of problems in the correct and harmonious alignment of the dental arch. Extracting an impacted tooth will prevent infection, damage to the bone and adjacent teeth.
The extraction of the teeth is also a useful method for orthodontic purposes, because it gives the possibility to create more space on the dental arch for the position of the teeth with serious repercussions in the process of developing occlusion, chewing and swallowing.
How can you delay tooth extraction?
In case, the anatomical features or other pathological processes permit, dentists may use the following auxiliary surgical methods to prolong the life of the natural tooth and delay dental extraction:
- Periapical curettage –is an endodontic surgical procedure that allows us to remove infected tissue from the periapical region (around the tip of the tooth root);
- Apicoectomy – involves the surgical removal of the apex (terminal part of the root of a tooth) and the infected bone tissue;
- Root amputation – consists in removing one or more roots of a tooth (multi-rooted), leaving only the part of the crown that corresponds to the root itself.
Pain and post-extraction advice
No one likes pulling out a tooth, as it is usually thought to cause pain. The modern dentistry and new discoveries in this area, have facilitated this process, managing to reduce the pain and discomfort that were common some time ago. Now dentists use anesthetic preparations which make this procedure more comfortable and eliminates or reduces pain and patient anxiety.
To avoid pain or discomfort after a tooth extraction, must follow all the advice of the dentist, some of them are:
- First, it is necessary to apply gauze on the wound and keep it pressed constantly, for 30 minutes, to facilitate blood clotting and stop bleeding. Cold packs and ice are very helpful in these situations.
- For a few days after a dental extraction, the consumption of hard, too hot or too cold foods should be avoided. This will reduce the possibility of causing injury in the extraction place.
- Immediately after tooth extraction, it is recommended to take painkillers and anti-inflammatories, because it may have pain or discomfort after the effect of the anesthesia passes. In some cases (for example when a complicated tooth extraction has been done) your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
- For at least 24-48 hours you should not chew, rinse or brush the operated area, as it could cause some trauma or break the sutures.
- It is important to not smoke for at least 24 hours after it was performed dental extraction, because smoking increases the risk of bleeding and delays healing.
Possible consequences after tooth extraction
- After tooth extraction it is normal to have bleeding and swelling. If bleeding is unusual 4-6 hours after surgery, you should contact your dentist immediately.
- The swelling occurs 24 hours after the operation and can last up to a week after the extraction. It can be relieved with ice packs on the cheek on the extraction side for 20 minutes, to be repeated every hour.
- Sometimes the patient feels discomfort when he opens his mouth. This is due to muscle spasms or trismus (inability to fully open the mouth), but this condition disappears after a few days.
Contraindications to dental extraction
In some situations, tooth extractions need to be temporarily postponed due to any adverse circumstances, for example:
- acute inflammatory processes due to diseased teeth, as in this situation the body creates a biological barrier between the site of the infection and the rest of the body, and tooth extraction would affect this barrier;
- in the case of acute rhinogenic sinusitis, tooth extraction is postponed until the inflammation decreases in intensity;
- in the case of stomatitis (affection of the oral cavity), because this mouth disease has a high concentration of microbes that can enter the body through a wound after tooth extraction;
- in myocardial infarction, dental extraction is contraindicated for 6 – 12 months after the onset of the heart attack;
- în cazul leucemiei acute;
- tooth extraction is not done for pregnant women in the first and third trimester;
- some treatments followed by patients such as anticoagulant treatments, chemotherapy, radiotherapy.
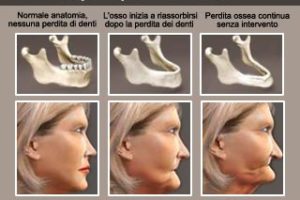
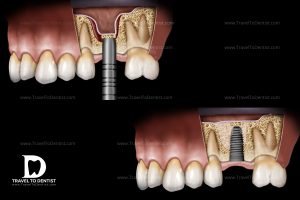
Before extracting the tooth, you will have to carefully evaluate the need for surgery. If tooth extraction is unavoidable, it is necessary to know the importance of replacing missing teeth; because the remaining teeth begin to move to fill the empty space resulting from the extraction of the tooth. Tutto questo spostamento può causare un morso vizioso e nel tempo questo può provocare dei problemi sull’occlusione. Displaced teeth are more difficult to clean and consequently poor hygiene will be the main reason for gum disease, cavities and increases the risk of tooth loss. Therefore, it is essential to replace missing teeth with bridges, dentures or dental implants.














Spelling error report
The following text will be sent to our editors: