What do we mean by tooth mobility?
Tooth mobility occur when the teeth move horizontally and / or vertically.
There are 2 types of dental mobility: physiological and pathological. It is called physiological mobility when teeth have a natural mobility, even in the absence of any disease. This is not visible to the naked eye. Pathological mobility (referred in this article) occurs when the teeth have become mobile for a reason and requires an individual approach to apply the correct treatment.

Until you reach the doctor, try to check by yourself if you have a loose tooth, so you can take action to save it early.
Why do teeth loosen?
Most patients are wondering why do teeth shift?
The most common causes are:
- Pathological like periodontitis and gingivitis (Find out here how they can be treated)
- Injuries (accidents)
- Aggressive bruxism
- Apical granulomas
- Incorrect occlusion (overcontacts)
- Compromised prosthetic works (large bridges on few pilar teeth)
- Mobile prostheses (attached to the remaining teeth that may eventually weaken them)
Consequences: What can happen if we don’t stop tooth mobility in time?
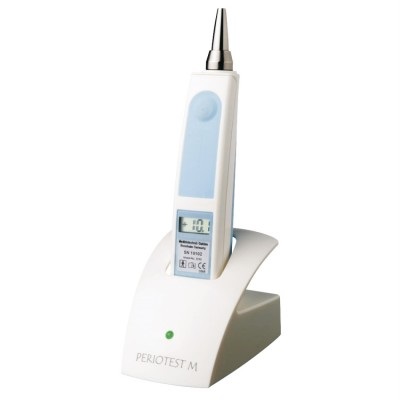
This is Periotest – is the instrument most commonly used for measuring osseointegration in dental implants, but it is also used to determine the mobility of the teeth or stability in the bone.
The weakening of stability of the tooth in the bone is slow. This process, in dentistry, has been studied by several doctors – scientists as: MUHELMANN, LINDH, ADA (the association of American dentists) and others. The most common and well-known classification is:
- Grade 0 – physiological mobility
- Grade 1 – when the teeth move more than 1 mm back and forth
- Grade 2 – when the teeth move more than 1 mm back and forth but also from right to left
- Grade 3 – when the teeth move in all 3 directions: forward-backward, right-left but from top to bottom
Today, the degree of mobility is highly appreciated with the device called “periotest” (successfully used in measuring the integration of the implants in the bone).
Stage 1 and 2 mobile teeth could be stabilized, but in case of stage 3, we need to apply more radical solutions.
The main consequence of teeth mobility is that the degree of mobility increases, and the roots expose more and more. For this reason will suffer: For this reason will suffer:
- Aesthetic appearance (the roots of the teeth are visible while you speak or smile)
- Occlusion (the harmonious dental contacts responsible for the chewing process and facial profile will disappear)
- The budget (the greater the degree of mobility, the more radical and expensive the solutions)

Although the mobility of the teeth is not observed by those around you however, this problem can be complex and will often get you out of comfort.
How do we stop the slight mobility and how we deal with increased mobility?
Tooth preservation should always be a priority for the doctors, but also for the patient. The correct and timely treatment can stop the mobility of the teeth, therefore we strongly recommend that you visit at least twice a year the dentist. He will identify the degree of mobility, and depending on this, he will propose you one of the solutions listed below:
For 1st degree mobility, it will be proposed:
- Fiberglass splinting
- Curettage (deeper cleaning of the roots of the teeth)
For 2nd degree mobility teeth, the cause that led to mobility will be analyzed individually. Possible solutions could be:
- Changing the compromised prosthetic work with more suitable solutions
If your teeth are moving in all 3 possible positions (forward-backward, right to left, up and down), then the solution will most likely be:
- Teeth extraction and replacement with dental implants, bridges (if the teeth are strong enough for this option), or mobile prostheses.
Price: How much will it cost to stabilize or replace your mobile teeth?
Each clinic or dentist sets different prices for dental services. European countries offer higher prices compared to countries outside the EU where dental tourism is practiced, and patients are able to save a lot.
For conservative treatments (applied to teeth that move less) the costs will be insignificant.
In our clinic in Moldova, we propose:
- dental splinting at the price of 20 euro per tooth
- Deep root cleaning(Curettage) at the price of 20 euro per tooth
- The price for prostheticsis 100 euro for each metal ceramic element of the bridge or 225 euro for each zirconium ceramic or all ceramic crown.
In case the degree of mobility is high and we can’t apply maintenance treatments, the only solution is the tooth extraction. From that moment on, the patient is facing another problem:partial edentation or total. Solving each one of them involves different options and costs.
















Spelling error report
The following text will be sent to our editors: