Periodontitis and pyorrhea. What are the differences between them?
Both periodontal diseases affect the ligaments and bone that surround and support the teeth. They are always confused because they affect the same tissues that surrounds and support the teeth. However, the differences between them are the symptoms, causes and methods of treatment.
Periodontitis manifests like an inflammation of the gums known as gingivitis. Untreated in time, the disease worsens in pyorrhea and destroys the surrounding tissues and support around the tooth root. With the evolution of the disease, periodontal pockets and bone resorption appear.
Pyorrhea is characterized by the absence of the inflammation and periodontal pockets. It is a severe condition of periodontal disease in which the ligaments and bones that support the teeth become inflamed and infected. Parodontoza se dezvoltă mai mult la persoanele cu boli cronice ca diabet, osteoporoza sau boli autoimune.
To better understand how periodontitis differs from periodontitis, look at the table below.
| periodontitis | Object of comparison | periodontitis |
| inflammatory process | short characterization | bone destruction |
| more common | spread | less common |
| it evolves very quickly with pronounced symptoms from the very first stages | evolution | slower evolution that develops years in a row |
| usually – poor dental hygiene | causes of occurrence | still not fully understood – supposed to be hereditary, chronic bone disease, diabetes. Under conditions of poor hygiene, periodontitis will evolve faster |
| 1 or more teeth | location | both arcades |
| bleeding gums is the main symptom and edema is present. In smokers, bleeding may be absent due to nicotine. | gum condition | In most cases, the gums are not inflamed or bleed. Edema is missing. |
| in the initial stages, mobility can be observed, but with a correct treatment it is completely stabilized | tooth mobility | In the initial stages – the teeth move very little. Mobility increases when the roots are more than half uncovered by the bone. |
| present | pain | absence |
| apply treatments to relieve symptoms and recovery is complete | rehabilitation | continuous treatment to maintain teeth and slow down the destructive process of bone |
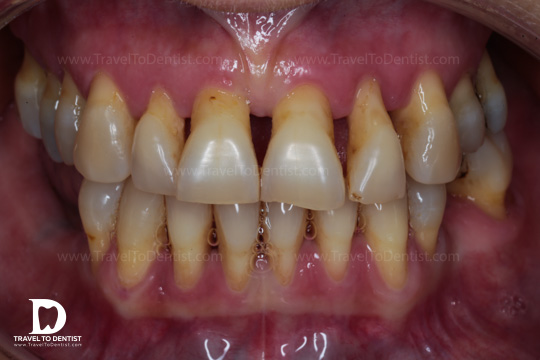
In this image, we notice the resorption of the bone and the roots of the teeth that were left exposed by the bone. Watch below how this case of periodontitis was solved.
What are the consequences of periodontitis and periodontitis?
Among the most important consequences of periodontitis and periodontitis we list:
- bone resorption;
In both periodontitis and periodontitis, the bacteria around the root of the tooth “eat” the bone, promoting its resorption.Read more about this phenomenon by clicking here. - withdrawal of the gum;
The gum retracts with the bone. In periodontitis we can see in some places the level of the gums that recede along the tooth, which highlights an uneven level. In periodontitis, the level of the gum recedes everywhere evenly. - root discovery;
Following bone resorption, the roots of the teeth are exposed more and more, thus remaining uncovered by the bone. In the case of periodontitis, the roots are discovered in the areas of the periodontal pockets. They can be located at one or more teeth. Periodontitis, on the other hand, usually affects all teeth, and their roots remain exposed all around. - tooth mobility;
Due to the bone destruction around the tooth, it is no longer well supported by the bone and becomes mobile. The mobility of the teeth affected by periodontitis can be observed in the initial stages, but it stabilizes quickly with a correct treatment. In the case of periodontitis, mobility is more pronounced and irreversible. - bad smell;
In both cases there is an unpleasant odor in the mouth. Periodontitis is more pronounced than periodontitis, however, despite this, the odor disappears with the treatment of infamous processes.
How do we treat periodontitis and periodontitis?
Periodontitis is very easily treated with a correct and timely treatment. Unfortunately, it is said that periodontitis is never treated, except by extraction.With the disappearance of the tooth, periodontitis also disappears. However, this is a radical measure and is applied when the periodontitis stage is advanced and the teeth move very hard. Read more about tooth mobility and their degree of mobility, as well as the stabilization solutions in the article ”tooth mobility”!
Treatments applied to periodontitis will treat the disease completely. Practically the same treatments can be applied in the case of periodontitis, in order to slow down its evolution, to stabilize the teeth somewhat or to improve the unsightly appearance of the teeth discovered by the bone and gums.
Measures to treat and slow down the development of periodontitis and periodontitis:
- curettage – deep cleaning of the roots of the teeth;
Curetage is performed to remove all deposits around the tooth and to polish the surface of the root. In this way, the bacteria stick harder to the root, which slows down the withdrawal of the bone. - flap operation – correction and restoration of periodontal pockets with artificial bone;
Flap surgery refers to the addition of artificial bone to periodontal pockets. This treatment will be applied more in the case of periodontitis than in the case of periodontitis. - plasmolifting;
Plasma injections are short-lived and aim to promote the process of growth and regeneration of gum cells. They can be applied in both periodontitis and periodontitis. The effects will be more visible only in the case of periodontitis. - antibiotic treatment.
Both diseases are affected by some bacteria. Like any other bacteria in the human body, they could be treated with antibiotics. In this case, thorough investigations and various tests will be done to detect the type of bacterium and the antibiotic that could destroy it.
Treatments for smokers may not respond as quickly as for non-smokers. The cure for periodontitis in smokers is slower, in some cases it may not even be completely treated.
Measures to reduce the consequences of periodontitis and periodontitis are:
- gnashing of teeth;
To stabilize the teeth with degree of mobility In addition, a group of 4-6 teeth will be signed with glass or metal wire on the inside of the teeth. Bleeding can be applied to both periodontitis and periodontitis. - prosthetic teeth through dental bridges;
To hide the exposed and sensitive roots of the teeth, they will be covered with dental bridges. This is not a treatment for periodontitis or periodontitis, but only to improve the appearance if it embarrasses you. - gingivectomy.
The gum transplant will be applied only in the case of periodontitis, where the gum level is withdrawn and uneven.
How much does it cost to treat periodontitis and periodontitis?
In the early stages of both diseases, treatment costs you little. With the aggravation of the problem and the discovery of bone roots, the price can increase to improve the aesthetic appearance of the teeth. The costs can increase even more if the teeth affected by severe periodontitis are removed and you decide to replace them with dental implants. Find in the article ”partial edentation” and ”total edentation” prices for replacing teeth with implants.
In non-EU countries where dental tourism is practiced, prices are at least 3 times lower than in European countries.
Our clinic offers you the following prices for treatments to slow down and reduce the effects of periodontitis:
- from 20 euro for each tooth for cleaning procedures;
- from 30 euro to 125 euro per tooth, it costs artificial bone for flap surgery;
- 120 euro for an entire arch costs the plasmo lifting treatment, the same could cost the treatment with antibiotics;
- 20 euro per tooth costs to grind the teeth to stabilize the teeth;
- 140 euro for a gum transplant;
- 100 euro per tooth costs a metal-ceramic dental crown to cover the teeth whose roots are exposed and sensitive.
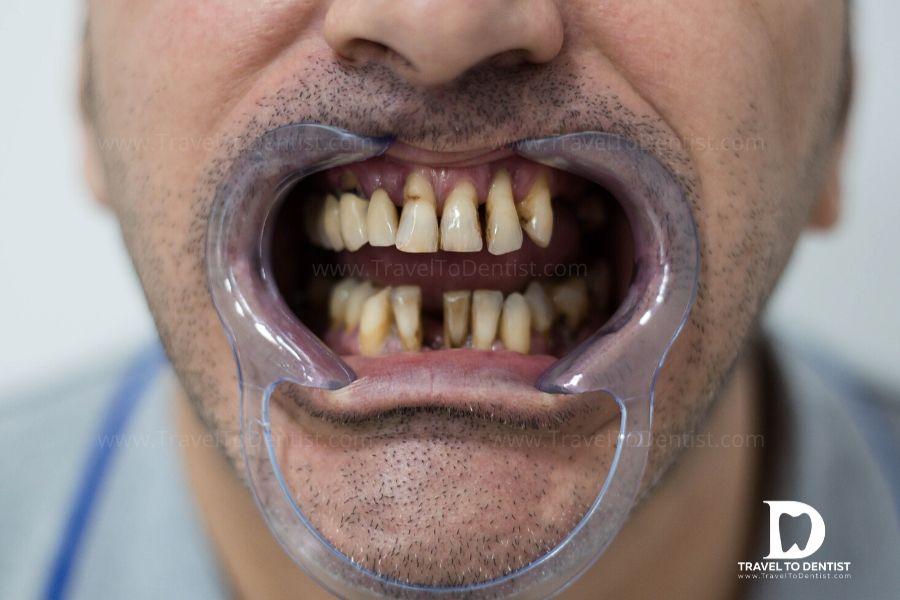
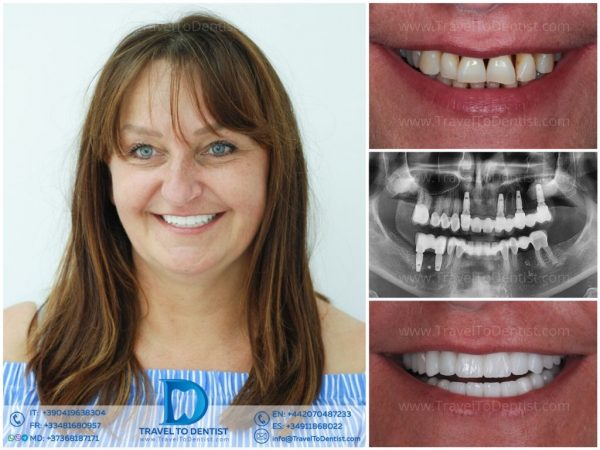
In the image below, we see the patient suffering from generalized periodontitis on both jaws. All teeth have second and third degree mobility. The solution proposed by us was the extraction and replacement with implants of the teeth with a high degree of mobility, and the other teeth were encapsulated and stabilized by dental bridges. All crowns are made of zirconium ceramic and fixed by “screwing”. The treatment was performed in 2 stages, and the final cost was three times lower than it would have cost in the home country. The patient moved from Belgium in our clinic in Moldova, where dental tourism has been practiced for 10 years. The clinic organizes your entire head-to-head. stay. If you like the result, do not hesitate to contact us.















Spelling error report
The following text will be sent to our editors: