 What is alveolar bone?
What is alveolar bone?
The alveolar bone is the bone where the roots of the teeth are positioned. He differs in many ways from other bones in the human body. Its important peculiarity is the ability to model itself over time, especially when teeth are missing, or when there is some periodontal disease.
The alveolar bone plays a very important role, namely that of maintaining the stability of the tooth .. When there is no longer the chewing load transmitted from the tooth to the alveolar bone (with the loss of teeth), the bone no longer performs its supporting function and is more prone to a decrease (it shrinks until it becomes completely thin)
What are the main causes of bone resorption?
We must also admit that the resorption of the alveolar bone occurs naturally, with aging– a normal and physiological process of the body. However, there are various factors that can contribute to and accelerate bone resorption, including:
- natural or accidental tooth loss, tooth extraction;
- periodontal diseases: periodontitis, pyorrhea;
- the disease of osteoporosis;
- infection and dental granuloma;
- trauma.
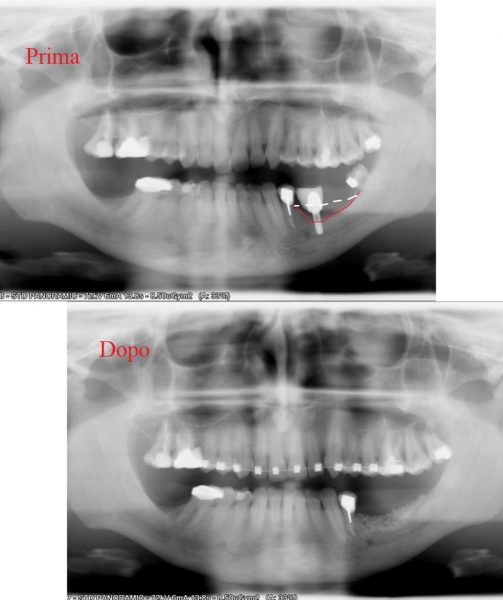
Radiography before and after. Case report of severe bone resorption on the lower jaw. Bone height was restored with natural bone block and artificial bone granules.
How to prevent bone resorption and how to get it back to normal?
- Before looking for solutions to prevent bone resorption, we need to know the cause of the bone loss. ?
- If it is a periodontal disease caused by bacteria,the necessary measures will be taken to treat it, such as professional subgingival cleaning performed on a regular basis.
- When the cause of bone resorption is a granuloma or an infection, then steps must be taken to treat them. In the article “Periodontitis” you will find more details about this problem.
- In most cases, the bone quickly begins to reabsorb due to tooth loss, so one ofthe solutions would be to replace the lost teeth as soon as possible. There are various possibilities to replace missing teeth (access the article ”Partial edentulous“to know them all), but the only method that can prevent bone loss is thedental implant. He represents an artificial titanium root that has the same role as a natural root, that is to maintain the alveolar bone that surrounds it.
2. Once the bone has resorbed, it is difficult to hope for growth in a natural way without resorting to bone regeneration techniques. Obviously with excellent oral hygiene, small bone defects (called periodontal pockets) could return to the normal / initial bone level. If the bone has shrunk considerably, bone grafting procedures should be used to reconstruct the lost height or thickness.
Nell’immagine sopra, notiamo un caso clinico di riassorbimento osseo e di seguito, il risultato di una ricostruzione ossea realizzat nella nostra clinica in Moldavia. The x-rays show the bone defect on the lower jaw and the final result following the bone reconstruction.
How does the passage of time affect bone resorption and the possibility of placing dental implants to obtain fixed teeth?
Following the loss of teeth,the alveolar bone begins to gradually reabsorb,losing height and thickness on average with 40-60% in the first 2-3 years, then continuing with a rate of 1% per year.
If you are missing any teeth, and you opt for their replacement with dental implants, you should be aware that the height and thickness of the bone is very important. If a lot of time has passed since the extraction of the teeth and if the alveolar bone has undergone evident bone resorption, then the implant surgery could become a little more complicated, but fortunately not impossible. Modern dentistry offers various solutions for obtaining fixed teeth, even if the jaw bone has lost its volume. Among these solutions, depending on the bone defect created, your doctor may suggest that you opt for:
- bone grafting;
- classic mini implant (conventional);
- all on 4 (the last implant on each side positioned under the corner);
- zygomatic implant;
- pterygoid implant;
- 2, 3 or even 4 classic implants inserted where there is more bone and semi-fixed prostheses on them.
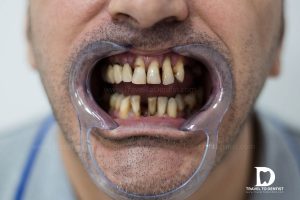
Bone loss can cause morphological, functional and aesthetic alterations Along with the bone loss, the roots of the teeth also expose and begin to move. If the mobility of the teeth is not stopped in time (click on the link of the article “The mobility of the teeth“, to discover all the ways to stabilize the mobile teeth), you risk being edentulous in the short term. After the loss of all teeth, the alveolar bone suffers large changes in its volume, and even classic dentures do not rest well on the bone crest and become really uncomfortable.
Bone loss over the years brings changes to the face profile. The lips become thinner, the skin loses its elasticity and so the wrinkles near the mouth and neck also increase, as you can see in the image above. Only a treatment done on time (dental implantology) can prevent the aged appearance and offer it the possibility of achieving the desired result, such as functionality, aesthetics of the teethand self-confidence
In the video below, you can notice all the changes that occur with tooth loss and resorption of the alveolar bone.















Spelling error report
The following text will be sent to our editors: